Silt and sedimentation are clogging our nation’s waterways and reservoirs. Years of fluctuating water levels, erosion, development, nutrient loading and decomposition of natural materials, have put these waters in dire need of improvements. Fish habitat, which includes habitat for countless other equally important aquatic organisms, lacks to the degree on many U.S, waters, that no amount of fish stocking can improve the fishery. Without adequate habitat, the fish simply cannot survive.

I met Shane Titus, Seneca Nation of Indians Fishery manager over three years ago as we began to talk about fish stocking, fluctuating water levels and ways of improving overall fish habitat on the Allegany River/Reservoir. Shane contacted me directly to understand more about our artificial habitat products and working together with ways to improve his local conditions. Here is a man with a unique perspective on Tribal rights as well as American U.S./State policies. Proudly having an Indian mother and Italian father, his gentle blend of both “sides”, make it evident that he is a special and highly qualified man for this job. His utmost concern is for the land, waters and the creatures within, helping sustain this natural environment, which breathtakingly surrounds himself and his people in western New York.

Shane understands the benefits of adding habitat. He has installed habitat structures in the reservoir for many years and has a quite impressive reputation as a fisherman. “Because the reservoir is so lacking of good habitat, almost anything you add will usually hold some fish.” Prime habitat for all animals, including fish, focuses around diversity. All of the same is rarely best, no different than we humans see things. A less stressful environment grows healthy beings and fish health also is directly related to the stress they encounter surviving from fry through adulthood.

To best understand a healthy fish habitat, imagine a large tract of mature hardwood forest, noticing the plants from tiny grasses and ferns, up to shrubs, bushes and trees. Countless shapes, textures, densities and elevations provide unlimited choices of surroundings, depending on creatures needs. Tiny bugs and insects, utilize the fine forest floor, hiding and grazing on the abundant food available. Birds eat berries and some of those bugs, from the lower branches of bushes and undergrowth, while they defensively watch for danger from above or below. Deer, rabbit, and other small game enjoy the shade from the undergrowth as they hunt or rest. The bigger the tract of forest, the more variety and abundance animals it can/will sustain. Fish habitat is no different than a mature and healthy forest, requiring infinite variety to support diversity and abundance.

Increasing fish habitat groupings on a large scale creates unique areas and corridors for fish to flourish and increase in numbers, not simply attracting a few fish to the area for potential fisherman/predator fish to enjoy. The surface area of the habitat grows the food (periphyton) with more area being best and essential to a healthy eco-system. Tight, dense shaded areas are essential for small fish to hide and graze within the protection the substrate offers. Dense, ultra-fine cover at the water’s edge restores the once healthy mass of roots and aquatic plants, grasses and invertebrates that young fish need. Natural weed beds and large rocks once provided this surface area for periphyton and algae to grow, but now they have been lost to sedimentation.

Titus was instrumental in obtaining a grant to help construct a new fish hatchery on the Reservation a few years back, which is now pumping out walleye and smallmouth fry annually for the Allegany.

His next goal was to get the financial help needed to begin to reclaim areas of the Allegany Reservoir that had been degraded. “We have almost no shallow cover left for the fry, due to erosion and siltation. Bays that lock in fish as they lower the water levels, killing everything left. We need to scoop that stuff out so they can navigate in and out like they used to be able to.”

As Shane continued to follow up on applications for various grant opportunities, our plans to work together to improve conditions on the Reservoir within the Reservation began to take shape. In late summer of 2014, notification was received of a grant award to the SNI from the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation being part of the Hurricane Sandy Coastal Resiliency grant funding. I got the call from Shane that his application was approved and how he was not only grateful, but quite humbled. “Our people could never have been able to afford and accomplish so much, so quickly, on a scale of this size. This will make a huge, positive impact on the fishery across miles.”

Plans were made to drive the 600 miles out to review the site, along with numerous models of our Fishiding artificial habitat. Decisions were to be made as to which artificial habitat models would be best, where the grouping would go and the overall quantities involved.
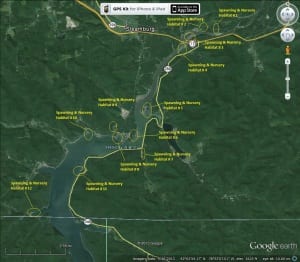
Fishiding.com produces artificial fish habitat from reclaimed PVC vinyl siding contained in a weighted base. Models from 18” tall up to 15 feet create unlimited variety, textures and densities of cover, creating a truly natural underwater landscape for aquatic life to thrive within. Over 2300 units consisting of five different models were selected totaling over 64,000 sq. ft. of surface area, ranging from 48”x84” to 18”x30” in size.
Means being used to document the habitats ability to provide sustainable habitat and deter erosion are by way of sonar equipment, water quality testing, underwater cameras and scuba certified staff. We (SNIFWD, USACE, USFS, and PAFBC) will be looking for signs of life such as invertebrates, algae growth, insect life, eggs of all life (insects, fish, amphibians, etc.) and any species of fish utilizing the habitat for shelter and food for research purposes and decision making for future habitat projects.

“It’s a no brainer as I see it,” said Titus. “Using this safe, durable, long-lasting material for fish habitat instead of buried in landfills, is a win for the people, fish and the environment. We can grow that stuff right into the shoreline, creating fry habitat and stabilizing the bank at the same time. We can plant them like balled bushes and watch them grow with life each year.”
I was welcomed by Shane and the team of conservation officers at the Fish and Wildlife Department who proudly work to sustain this pristine land they call home. A first-hand view of the Reservoir in November, Shane showed me the areas that we had talked about, in dire need of restoration.
We walked the river edge, casting jigs for some feisty walleye and smallmouth, catching a few and releasing them back to swim away. “ I keep a couple here and there, but they still feel like my babies” Shane explained, after raising and releasing hundreds of thousands of fry from the SNI Hatchery facility he operates on the Reservation, releasing them into the Reservoir. He showed me areas devoid of cover, after erosion and low water had worn away the plants, depositing sediment where rock/rubble once exposed. Huge bays landlocked, explaining how many fish die each year, being stuck with no way out as water levels drop, despite volunteers and staff netting and saving thousands of fish each season. Water marks so high, trees and plants were washed away, only to leave the water’s edge barren for fish to contend with in the spring as they attempt to successfully spawn.

Needless to say, excitement grew with the dream of being able to work along the river on a very large scale. To install thousands of individual habitat units creating tens of thousands of square feet of surface area would boost the fishery measurably. Concentrating on shoreline stabilization and fry recruitment, all targeting depths from 6 feet of water and under for the little fish, bugs and plant growth. Another additional benefit of large groupings of habitat is the excrement discarded by the fish and creatures that inhabit it fertilizing plant growth. Clearly aquatic growth, grass and weeds take root in the surrounding lake floor, being fertilized by the fish from above. Another win-win for the fish and the environment.

Project Abstract
The goal of this funding through established partnerships with the PAFBC, USFS, ACE will be to restore the habitat within the reservoir and create an enhanced water system that can tolerate high water events with minimal loss to wildlife and habitat.
The Seneca Nation of Indians has a long history of struggling to maintain its land base and yet there remains a unique and harmonious relationship between indigenous people and the concept of environmental sustainability. The Seneca people believe fully in the tenet of their forefathers, that everyone must plan for the future generations, up to and beyond the seventh generation. The current conditions that exist within the Allegany Reservoir create an intolerable struggle within the people as they are forced each year after year to witness thousands of fish dying, species disappearing or become species of concerns, a vital wildlife habitat lost. Over the past 60 years this reservoir has had numerous high water systems into the reservoir, suffocating aquatic species. Each event results in species lost, habitat lost, channels filled and community flooding.
The people of the Seneca Nation live and work on the same lands today that the Seneca people have inhabited for over 1000 years. The Seneca Nation holds title to five distinct but non-contiguous territories located in western New York, an area of the state where communities are primarily rural in geographic location. The territories are unique in its economic, social and environmental profile. With 53,884 acres, the Seneca Nation controls and holds a significant land base in western New York.
“The Allegany River/Reservoir Restoration and Resiliency Project”
Objectives/Outputs/Outcomes:
- Create a healthier habitat for aquatic species within the Allegany Reservoir
- 10 acres will receive in stream habitat restoration efforts.
- 50 acres will benefit from artificial and natural habitat structures.
- Enhance the flood plain and habitat restoration of the Allegany Reservoir through riprarian buffer restoration.
- 18.94 miles will have large debris removed from shoreline area.
- 10 acres will receive indigenous plantings.
- Restore hydrology to land locked areas of the Allegany Reservoir.
- 7 land locked areas will be reconnected to the Allegany Reservoir.
- 15 acres will be cleaned of sediment, silt and nutrients.
The habitat has been delivered and equipment is in place. Over the next two years, Shane and his team will work all year around, improving the many areas covered within the grant. A great deal of the work will be during the winter months, when water levels are down and lakebed areas exposed. The team will use an earth auger to drill/install the many pole clusters to be installed to regain a plant base in the many washes, streams and creeks flowing into the reservoir. These barriers will catch debris during runoff, creating a medium for plants to begin to take hold. Dozers, trucks along with a good amount of manpower will begin to remove the 1000’s of cubic yards of sediment from the bays and openings, allowing the fish to again, freely pass.

The artificial habitat units will be planted individually in shallow, drilled holes and backfilled like a balled bush. Planted in large clusters, these units will become exposed each year as the water levels drop in the fall, but take on new life each spring as water levels rise and fish move in to seek spawning protection. Not only will the shallowest models protect fish, but allow shoreline plants and their roots to attach and take hold, strengthening and buffering the eroded shallows. With this substrate in place, only good things follow.

Late in 2014, the Seneca Nation hosted its third annual “Allegany Reservoir Management Meeting”. Agencies that are represented at these meetings are: SNI Fish and Wildlife, SNI Administration Representatives, Pennsylvania Fish and Boat Commission, New York State department of Environmental conservation, US Army Corp of Engineers, ( KInzua staff, Pittsburg District), US Fish and Wildlife Service (Tribal Liaison, Great lakes rep., Hatchery Lamar PA, and Hatchery Kinzua PA), US Forest Service and California University of Pennsylvania. Topics discussed at these meetings are all the topics mentioned in the grant, plus stocking strategies, fish sampling surveys, fish pathology and funding opportunities. These “first of their kind” meetings are a shared water body being managed as a single water body.
Aquatic species that will benefit from the habitat are: Walleye (tribally significant species to Seneca culture and heritage) Smallmouth Bass, Large Mouth Bass, Black Crappie, White Crappie, Paddlefish (endangered), Northern Pike, Muskellunge, White Bass, Yellow Perch, Bullhead, Channel Catfish, Sunfish, Rock Bass, Sucker, Emerald Shiner, Golden Shiner, Fathead minnows, Spot Tail Shiner and Bluegill, Fresh Water Jelly fish, Aquatic spiders and Macro invertebrates.
Wildlife also benefitting from the habitat: Bald eagle, Golden Eagle, Cormorants, Loons, Ducks (all species), Canadian Goose, Osprey, Green Heron, Blue Heron, Snapping Turtle, Painted Turtle, Leather Back Turtle, Hellbender (amphibian, species of concern) and River Otter (species of concern)
Increased stewardship among the Seneca community will be an immeasurable benefit of this project. The SNI Fish and Wildlife Staff provide educational programs directed at youth to teach them about the environment and its importance to the health of all fish and wildlife. The SNI Fish and Wildlife Department plans on using these projects to create a three year educational tool for the youth and general public. The Seneca nation newsletter will be doing periodic articles to keep the public informed and involved in all aspects of the projects, to include the purpose, reasons, and outcomes of the work.
For more information regarding Reservoir habitat restoration, funding and other projects taking place, visit Friends of Reservoirs, which SNI Fish and Wildlife and Fishiding strongly support. Friends of Reservoirs (FOR), is a tax-deductible non-profit foundation dedicated to protecting and/or restoring fisheries habitat in reservoir systems nationwide. FOR is the funding arm of the Reservoir Fisheries Habitat Partnership, an organization of natural resource professionals and industry representatives, associated with the National Fish Habitat Partnership. FOR is also a coalition of local citizen groups dedicated to improving fish habitat in reservoir systems. David Ewald/ Fishiding.com
Underwater photography by Eric Engbretson, all rights reserved. For a complete library of Fishiding habitat underwater in various locations and conditions see Eric’s work here. Watch for much more information, photos and reports as this project gains momentum. We will be making many trips back to see Shane and his crew improving conditions on the Reservation. Fishing poles and tackle must be present for “testing”.


































 Friday, March 8, 2013 at 9:21AM ActivistAngler.com
Friday, March 8, 2013 at 9:21AM ActivistAngler.com